Strategies for change data capture in dbt
There are many reasons you, as an analytics engineer, may want to capture the complete version history of data:
- You’re in an industry with a very high standard for data governance
- You need to track big OKRs over time to report back to your stakeholders
- You want to build a window to view history with both forward and backward compatibility
These are often high-stakes situations! So accuracy in tracking changes in your data is key.
If you’ve encountered this problem before, you know it’s a tricky one. dbt is idempotent - it recreates tables at runtime with the CREATE TABLE AS syntax. Because of this, the ability to access a full picture of historical outputs isn't intrinsic to dbt.
Let’s imagine a specific scenario. Joanne is an analytics engineer for a large e-commerce company. The head of sales just messaged her the following question:
“Can you tell me the income for January 2022 for all clothing products?”
On the surface, this may seem like a simple question. But what if the calculation of income has changed since January 2022? Should Joanne calculate the income using the current formula or the formula that was used in January 2022? What if the source data for January changed after the month closed? Should Joanne use the source data as it was on January 30th, 2022 or the source data as it is now?
All of these questions bubble up to our main theme: How can you capture historical versions of our data using dbt?
Sorry, Joanne. The TL;DR is - “it depends.”
When I first encountered this problem, it took time and effort to:
- think through the possible solutions
and
- determine which solution best suited my needs
The goal of this article is to eliminate step one – to provide you with a menu of solutions I’ve encountered so you can spend less time ideating and more time considering the nuances of your specific use-case.
I’ll start by discussing a basic version of the scenario I first encountered – a ⚠️ misapplication ⚠️ of dbt’s snapshot functionality. Then, I’ll outline a couple of solutions:
- Downstream Incremental Model: Build an incremental model downstream of the model which contains your business logic to “grab” every point-in-time version
- Upstream Snapshots: Build snapshots on all of your sources to capture changes in your raw data and calculate all versions of history every time you execute a
dbt run
Finally, I’ll discuss the pros and cons of each solution to give you a head start on step two.
Scenario
Let’s return to Joanne. Using dbt and her favorite BI tool, Joanne has created an income report to track monthly income for each product category.
You can imagine her DAG as shown below, where fct_income captures income per month for each product category.
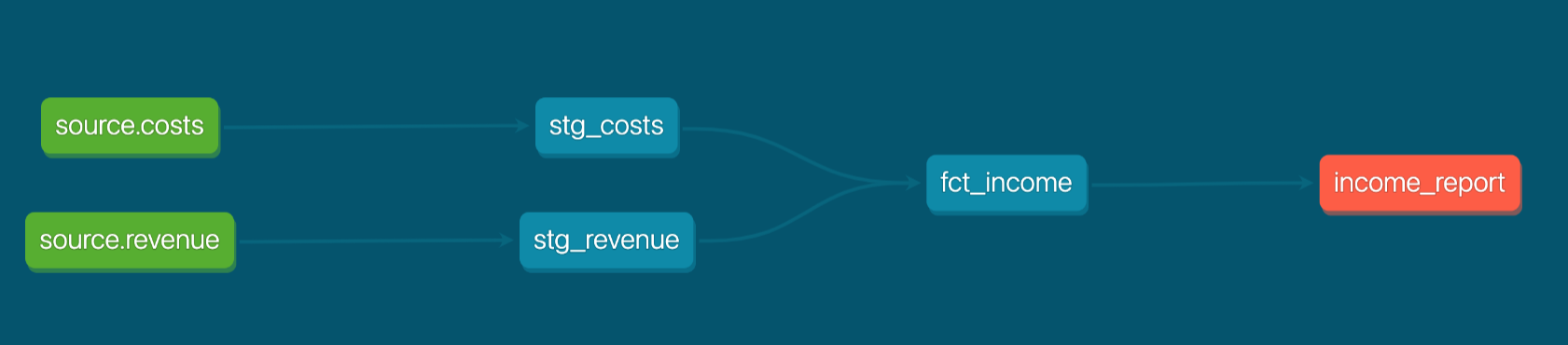
Joanne executes a dbt run on January 30th, 2022 and queries the resulting table:
select * from fct_income where month_year = "January 2022"
She gets the following output:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
But a few days later, her source data changes for January - a manufacturing cost was dated incorrectly, and now has been updated in the source. Joanne executes a dbt run again on February 3rd. Now when she queries fct_income, she gets the following output:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 200 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
A few days later, Joanne finds a bug in her dbt code. She fixes the bug and executes a dbt run again on February 10th. Now, when she queries fct_income, she gets the following output:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 202 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
When the head of sales messages Joanne the following question: “Can you tell me the income for January 2022 for all clothing products?”, she’s unsure which number to give: 100, 50, or 52.
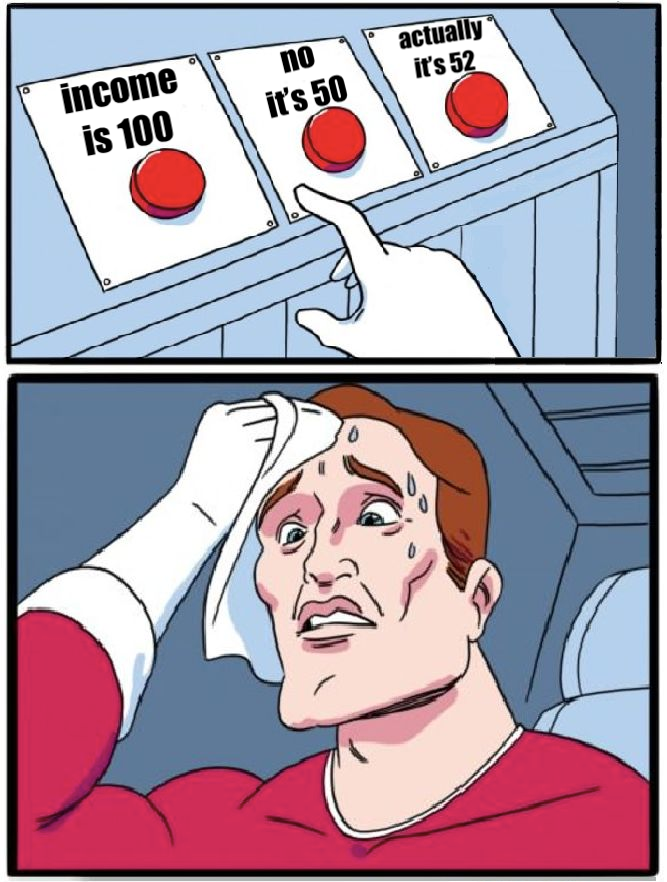

Because of this complexity, she decides to capture the history of her income report so that she can easily swap between versions in her BI tool.
Her goal is to capture all versions of the fct_income model for January. Something like this:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 300 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 |
| January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 200 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 | books | 202 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
In order to achieve this long table of history, she decides to start snapshotting her final model, fct_income.
I'm including the code samples for completeness, but remember: the method described in this scenario of snapshotting a final model contradicts dbt Labs' best practices. Either of the solutions detailed later is a better approach.
{% snapshot snapshot_fct_income %}
{{
config(
target_database='analytics',
target_schema='snapshots',
unique_key='id',
strategy='check',
check_cols=['income']
)
}}
select
month_year || ' - ' || product_category as id,
*
from {{ ref('fct_income') }}
{% endsnapshot %}
The output of snapshot_fct_income looks like this:
| id | month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp | dbt_valid_from | dbt_valid_to |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 - clothing | January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 - electronics | January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 - books | January 2022 | books | 300 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 |
| January 2022 - clothing | January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 - electronics | January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 - books | January 2022 | books | 200 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 |
| January 2022 - clothing | January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | NULL |
| January 2022 - electronics | January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | NULL |
| January 2022 - books | January 2022 | books | 202 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | NULL |
Each month now has multiple versions of income, and the sales department is responsible for determining which version is “correct.”
In order to keep track of which version has been marked as “correct” by the sales department, Joanne creates a seed file to capture which version of the fct_income model is the correct one for each month. The output of her seed income_report_versions looks like this:
| month_year | correct_version | comment |
|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | Approved by Lucy |
Her final DAG now looks like this:

She's snapshotting fct_income, joining the seed file with the snapshot, then exposing the final output to her BI tool. The final output of stg_snapshot_fct_income looks like this:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp | correct_version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 300 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 200 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | books | 202 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
This method technically works. Joanne can track what she needs:
- source data changes
- business logic changes
And she can easily switch versions by adding a filter on her BI layer.
However, this method causes long job times and adds potentially unnecessary complexity – one of the reasons our best practices recommend only using snapshots to track changes in your source data, rather than your final models.
Below, you’ll find two solutions that are more effective than snapshotting a final model, as well as the pros and cons of each method.
Solution #1: Downstream Incremental Model
Instead of using snapshots, Joanne could create an incremental model downstream of fct_income to “grab” every point-in-time version of fct_income – let’s call this incremental model int_income_history and assume it has the following config block:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental'
)
}}
By materializing int_income_history as incremental but not including a unique_key config, dbt will only execute INSERT statements – new rows will be added, but old rows will remain unchanged.
The rest of int_income_history would look like this:
...
select
*
from {{ ref('fct_income') }}
{% if is_incremental() %}
where true
{% endif %}
There are a few additional configs that Joanne might find helpful:
- she can use the
on_schema_changeconfig to handle schema changes if new columns are added and/or deleted fromfct_income - she can also set the
full_refreshconfig to false in order to prevent accidental loss of the historical data - she can build this table in a custom
schemaif she wants to enforce specific role-based permissions for this historical table - she can specify a time-grain
unique_keyif she wants to reduce the amount of versions being captured- for example, if she only wants to capture the final version of each day she could set
unique_key = date_trunc('day', run_timestamp). This is excluded from the example below, as we are making the assumption that Joanne does indeed want to capture every version offct_income
- for example, if she only wants to capture the final version of each day she could set
The final config block for int_income_history might look something like this:
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
full_refresh=false,
schema='history',
on_schema_change='sync_all_columns'
)
}}
As a final step, Joanne would create fct_income_history to join in the seed file to determine which versions are “correct”. Her new DAG looks like this, where int_income_history is an incremental model without a unique key:

The final output of fct_income_history would look identical to stg_snapshot_fct_income from her initial approach:
| month_year | product_category | income | run_timestamp | correct_version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 300 | 01/30/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 200 | 02/03/22 16:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | books | 202 | 02/10/22 08:00:00 | TRUE |
Solution #2: Upstream Snapshots
Alternatively, Joanne could snapshot her source data and add flexibility to her modeling so that all historical versions are calculated at the same time. Let’s look at our example.
Joanne could track changes in the source data by adding snapshots directly on top of her raw data.

This would change the grain of these stg_ tables, so she would see a row for each version of each field. The staging models will contain the history of each record.
Remember the source data change Joanne noticed — a manufacturing cost was dated incorrectly (Junkuary 2022 instead of January 2022). With this solution, the costs_snapshot model will pick up this change:
{% snapshot costs_snapshot %}
{{
config(
target_database='analytics',
target_schema='snapshots',
unique_key='cost_id',
strategy='timestamp',
updated_at='updated_at'
)
}}
select * from {{ source('source', 'costs') }}
{% endsnapshot %}
| cost_id | month_year | cost | updated_at | dbt_valid_from | dbt_valid_to |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Junkuary 2022 | 50 | 01/15/22 12:00:00 | 01/15/22 12:00:00 | 02/03/22 12:00:00 |
| 1 | January 2022 | 50 | 02/03/22 12:00:00 | 02/03/22 12:00:00 | NULL |
Because snapshots only capture changes detected at the time the dbt snapshot command is executed, it is technically possible to miss some changes to your source data. You will have to consider how often you want to run this snapshot command in order to capture the history you need.
The original fct_income model now calculates the income for each version of source data, every time Joanne executes a dbt run. In other words, the downstream fct_ models are version-aware. Because of this, Joanne changes the name of fct_income to fct_income_history to be more descriptive.
In order to track changes in business logic, she can apply each version of logic to the relevant records and union together.
Remember the bug Joanne found in her dbt code. With this solution, she can track this change in business logic in the stg_costs model:
-- apply the old logic for any records that were valid on or before the logic change
select
cost_id,
...,
cost + tax as final_cost, -- old logic
1 || ‘-’ || dbt_valid_from as version
from costs_snapshot
where dbt_valid_from <= to_timestamp('02/10/22 08:00:00')
union all
-- apply the new logic for any records that were valid after the logic change
select
cost_id,
...,
cost as final_cost, -- new logic
2 || ‘-’ || dbt_valid_from as version
from costs_snapshot
where to_timestamp('02/10/22 08:00:00') between dbt_valid_to and coalesce(dbt_valid_from, to_timestamp('01/01/99 00:00:00'))
| cost_id | month_year | cost | tax | final_cost | version |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Junkuary 2022 | 50 | 1 | 51 | 1 - 01/15/22 12:00:00 |
| 1 | January 2022 | 50 | 1 | 51 | 1 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 |
| 1 | January 2022 | 50 | 1 | 50 | 1 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 |
The contents of the seed income_report_versions would look slightly different to match the change in version definition:
| month_year | correct_version | comment |
|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | 2 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | Approved by Lucy |
After joining in the seed file (check out Tackling the complexity of joining snapshots), her new DAG looks like this:
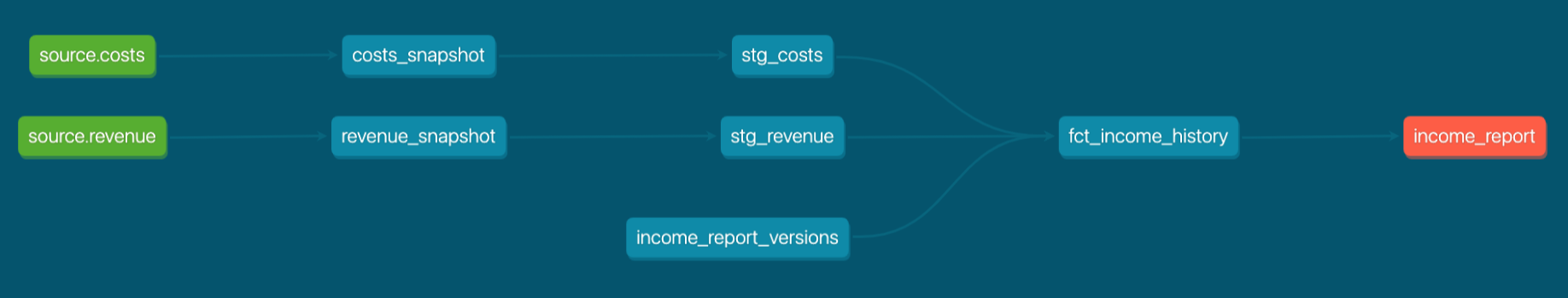
The final output of fct_income_history would accomplish the same goal as stg_snapshot_fct_income from her initial approach:
| month_year | product_category | income | version | correct_version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2022 | clothing | 100 | 1 - 01/15/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 200 | 1 - 01/15/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 300 | 1 - 01/15/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 50 | 1 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 150 | 1 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | books | 200 | 1 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | FALSE |
| January 2022 | clothing | 52 | 2 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | electronics | 152 | 2 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | TRUE |
| January 2022 | books | 202 | 2 - 02/03/22 12:00:00 | TRUE |
Final thoughts
Both of these solutions allow Joanne to achieve her desired output – a table containing all versions of income for a given month – while improving the workflow and the efficiency of the final model.
However, each has its advantages and disadvantages.
Solution #1: Downstream Incremental Model
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| incremental models without unique keys are fast | this isn't really the intended use of the incremental materialization |
| Joanne has no way to re-calculate prior versions if her historical table is accidentally lost |
Solution #2: Upstream Snapshots
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Joanne doesn't have to worry about losing historical data | snapshots are highly complex and require more institutional knowledge for Joanne's team |
| every time Joanne wants to make a code change that affects her calculations, she'll have to remember to apply the change to each set of relevant records and union the outputs together |
When deciding between the two solutions, you should consider the following:
- How often is your source data changing?
- How many bug fixes do you anticipate?
- How fast do you need this job to be?
- How much visibility do you need into why a change in historic values occurred?
💡 What do you think? Is there another, more optimal, solution?

Comments