dbt Cloud Architecture
This page helps practitioners and those interested in dbt Cloud's architecture and data flow.
About dbt Cloud architecture
The dbt Cloud application has two types of components: static and dynamic. The static components are always running to serve highly available dbt Cloud functions, like the dbt Cloud web application. On the other hand, the dynamic components are created ad-hoc to handle tasks such as background jobs or requests to use the IDE.
dbt Cloud is available in most regions around the world in both single tenant (AWS and Azure) and multi-tenant configurations.
dbt Cloud uses PostgreSQL for its backend, S3-compatible Object Storage systems for logs and artifacts, and a Kubernetes storage solution for creating dynamic, persistent volumes.
All data at rest on dbt Cloud servers is protected using AES-256 encryption.
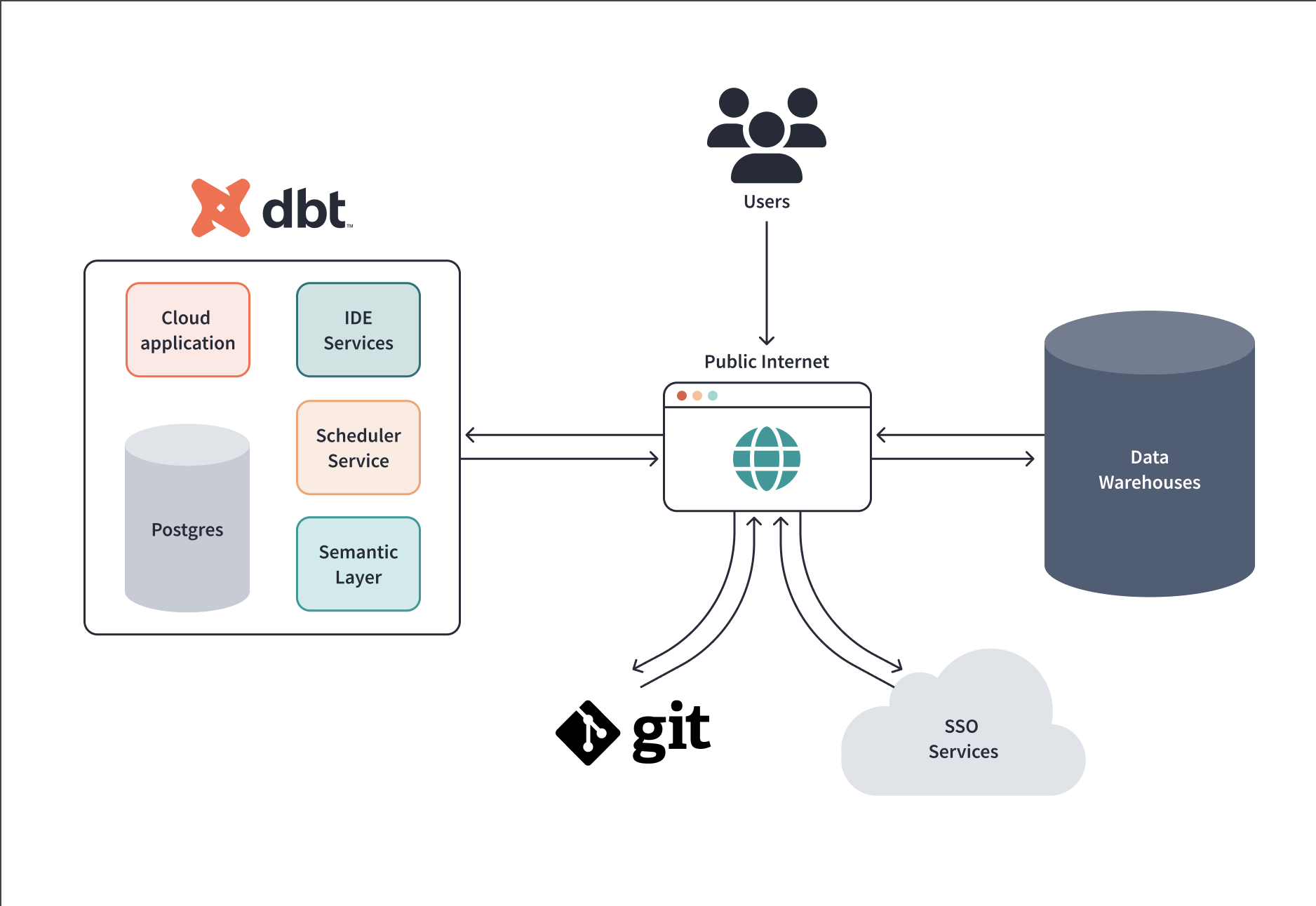
For a more detailed breakdown of the dbt Cloud apps, download the advanced architecture guide PDF.
Communication
dbt Cloud can communicate with several external services, including data platforms, git repositories, authentication services, and directories. All communications occur over HTTPS (attempts to connect via HTTP are redirected to HTTPS). dbt Cloud encrypts in transit using the TLS 1.2 cryptographic protocol.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1.2 is an industry-standard protocol for encrypting sensitive data while it travels over the public internet (which does not offer native encryption).
A typical scenario that might be seen frequently is an employee working in a public space, such as an airport or café. The user might be connected to an unsecured public network offered by a facility to which many others are also connected. What if there is a bad actor amongst them running a program that can "capture" network packets and analyze them over the air?
When that user is accessing dbt Cloud and running models that interact with the data platform, the information sent to and from their computer and the services is encrypted with TLS 1.2.
If that user runs a command that initializes communication between dbt Cloud and the data warehouse (or a git repo or an auth service) over the internet, that communication is also encrypted. This means that while the bad actor can technically see the traffic moving over that unsecured network, they can't read or otherwise parse any information. They will not be able to eavesdrop on or hack the information in any way whatsoever. They would see a nonsensical set of characters that nobody can decrypt.
For more detailed information on our security practices, read our Security page.
Data warehouse interaction
dbt Cloud's primary role is as a data processor, not a data store. The dbt Cloud application enables users to dispatch SQL to the warehouse for transformation. However, users can post SQL that returns customer data into the dbt Cloud application. This data never persists and will only exist in memory on the instance for the duration of the session. To lock down customer data correctly, proper data warehouse permissions must be applied to prevent improper access or storage of sensitive data.
Some data warehouse providers offer advanced security features that can be leveraged in dbt Cloud. PrivateLink allows supported data platforms on AWS to communicate with dbt Cloud without the traffic traversing the public internet. Snowflake and BigQuery offer Oauth integration which adds a layer of security for the data platforms (Enterprise plan only).
Git sync
dbt Cloud can sync with a variety of git providers, including Github, Gitlab, and Azure DevOps within its integrated development environment (IDE). Communication takes place over HTTPS rather than SSH and is protected using the TLS 1.2 protocol for data in transit.
The git repo information is stored on dbt Cloud servers to make it accessible during the IDE sessions. When the git sync is disabled, you must contact support to request the deletion of the synced data.
Authentication services
The default settings of dbt Cloud enable local users with credentials stored in dbt Cloud. Still, integrations with various authentication services are offered as an alternative, including single sign-on services. Access to features can be granted/restricted by role using RBAC.
SSO features are essential because they reduce the number of credentials a user must maintain. Users sign in once and the authentication token is shared among integrated services (such as dbt Cloud). The token expires and must be refreshed at predetermined intervals, requiring the user to go through the authentication process again. If the user is disabled in the SSO provider service, their access to dbt Cloud is disabled, and they cannot override this with local auth credentials.
Snowflake and BigQuery offer OAuth (JSON to pass info and API calls for auth) services as an alternative to SAML (XML to pass info and session cookies for auth). Users can authenticate against the data platform for secure access to dbt Cloud and prevent access when credentials are revoked.
Security
dbt Labs is dedicated to upholding industry standards for Cloud security and GDPR compliance. Our compliance certifications include the following:
- SOC2 Type II — assesses a service provider’s security control environment against the trust services principles and criteria set forth by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).
- ISO27001:2013 — a globally recognized standard for establishing and certifying an information security management system (ISMS).
- GDPR - dbt Labs is committed to maintaining GDPR compliance standards. Read more about our Data Processing Addendum.
For more detailed information about our security practices, read our Security page.